Factors Influencing Utility Costs
Utility costs for a 1-bedroom apartment can vary significantly, influenced by a multitude of factors. These factors can create a complex tapestry of expenses, making it crucial to understand their impact on your monthly bills.
Location
The location of your apartment plays a significant role in determining your utility costs. Cities with colder climates, like Chicago or New York City, will generally have higher heating costs due to the need for extended heating seasons. Conversely, cities in warmer climates, such as Miami or Los Angeles, will have lower heating costs but may have higher cooling costs during the summer months.
Climate
Climate directly impacts utility costs, particularly heating and cooling. Colder climates require more energy for heating, leading to higher gas or electricity bills. Conversely, warmer climates require more energy for cooling, resulting in higher electricity bills.
Apartment Size
The size of your apartment significantly impacts utility costs. Larger apartments generally require more energy to heat and cool, leading to higher utility bills. For example, a 1-bedroom apartment in a smaller building might have lower utility costs than a 1-bedroom apartment in a larger building.
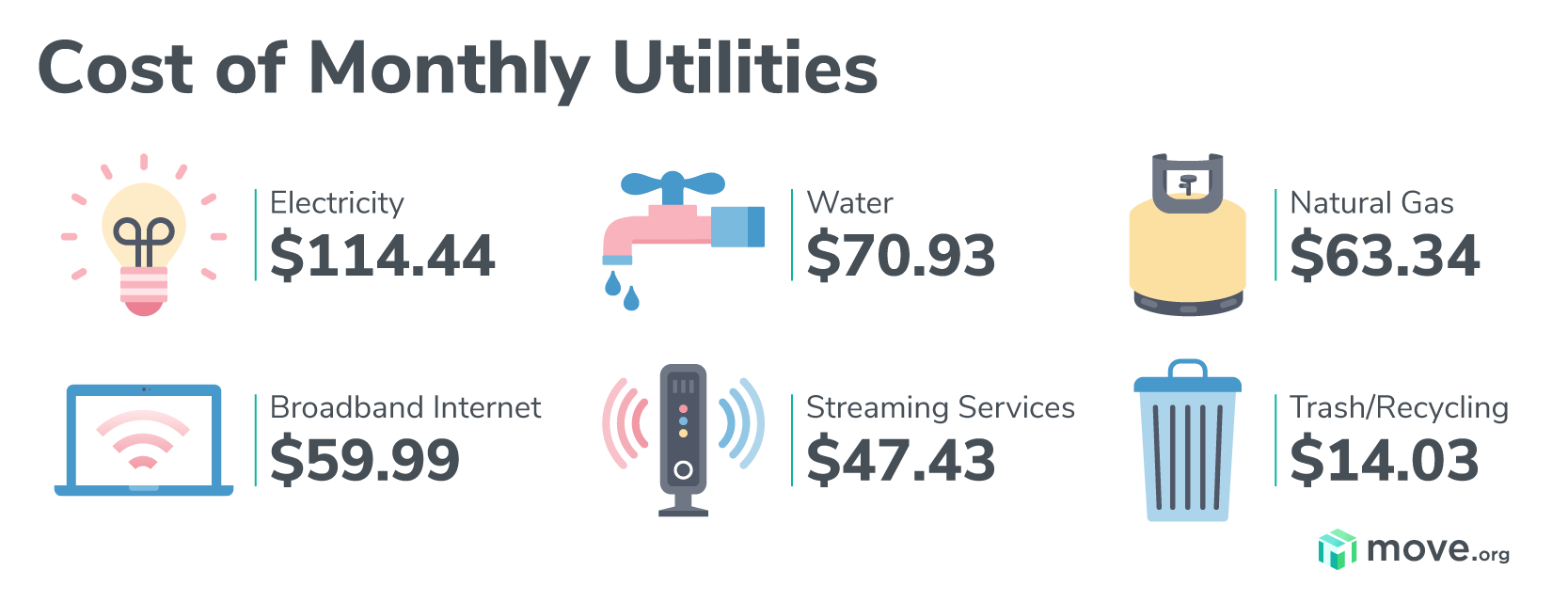
Building Efficiency, Average monthly utilities for 1 bedroom apartment
The efficiency of your building can significantly impact utility costs. Newer buildings often have better insulation and energy-efficient appliances, which can lead to lower utility bills. Older buildings, however, may have outdated insulation and appliances, resulting in higher energy consumption and higher utility costs.
Utility Expenses
Typical utility expenses for a 1-bedroom apartment include electricity, gas, water, trash, and sometimes internet.
- Electricity: Electricity is used for lighting, appliances, and heating and cooling systems. Average monthly costs can range from $50 to $150 depending on the size of the apartment, usage habits, and local electricity rates.
- Gas: Gas is primarily used for heating and cooking. Average monthly costs can range from $30 to $100 depending on the size of the apartment, usage habits, and local gas rates.
- Water: Water is used for showering, washing dishes, and laundry. Average monthly costs can range from $30 to $70 depending on the size of the apartment and usage habits.
- Trash: Trash collection is typically included in rent or charged as a separate fee. Average monthly costs can range from $10 to $30 depending on the location and the service provider.
Understanding Utility Bills

Utility bills are a necessary expense for any apartment dweller, but they can be confusing and sometimes even seem a bit mysterious. Decoding the components of your bill and understanding how they are calculated can help you better manage your budget and make informed decisions about your energy consumption.
Utility Bill Components and Calculations
The components of your utility bill will vary depending on your location and the specific services you use. However, some common components include:
- Energy charges: These charges reflect the amount of electricity or gas you have consumed. They are typically calculated based on a tiered system, where the price per unit of energy increases as your consumption rises. For example, you might pay a lower rate for the first 500 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity you use and a higher rate for any consumption beyond that.
- Water and sewer charges: These charges reflect the amount of water you have used and the cost of treating and disposing of wastewater. They are often calculated based on a fixed rate per unit of water used, with additional charges for sewer services.
- Trash removal charges: These charges are typically a fixed monthly fee for the removal of your household waste.
- Other charges: This category can include a variety of fees, such as late payment fees, meter reading fees, or charges for additional services like recycling or composting.
Fixed and Variable Utility Costs
Utility costs can be categorized as either fixed or variable:
- Fixed costs: These costs remain the same each month, regardless of your usage. Examples include basic service charges, meter rental fees, and some trash removal fees.
- Variable costs: These costs fluctuate based on your actual usage. Examples include energy charges, water and sewer charges, and charges for additional services like recycling or composting.
Utility Meters and Their Benefits
Utility meters are devices that measure your consumption of different utilities. They provide accurate readings that are used to calculate your utility bills. There are different types of utility meters, including:
- Traditional meters: These meters are typically read manually by a utility worker, which can lead to inaccuracies and inconsistencies in billing.
- Smart meters: These meters transmit readings wirelessly to the utility company, providing real-time data on your consumption. This allows you to monitor your usage, identify potential leaks or inefficiencies, and make adjustments to reduce your bills.
Average Monthly Utility Costs for a 1-Bedroom Apartment
The following table shows estimated average monthly utility costs for a 1-bedroom apartment in different types of housing:
| Housing Type | Average Monthly Utility Costs |
|---|---|
| Studio | $150 – $250 |
| 1-Bedroom | $175 – $300 |
| 2-Bedroom | $200 – $350 |
Note: These are just estimates, and actual costs may vary depending on your location, energy consumption habits, and specific utility providers.
Tips for Reducing Utility Costs: Average Monthly Utilities For 1 Bedroom Apartment

Reducing your utility costs in a 1-bedroom apartment can significantly impact your monthly budget. By implementing a few simple changes and adopting energy-saving habits, you can lower your electricity, gas, and water bills. This section explores practical tips and strategies for minimizing your utility expenses.
Conserving Energy and Water
- Unplug Electronics: Leaving electronics plugged in, even when not in use, consumes phantom energy. Unplugging devices like phone chargers, laptops, and TVs when not in use can reduce your electricity bill.
- Switch to LED Lighting: LED light bulbs consume significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs, saving you money on your electricity bill. They also last longer, reducing the frequency of bulb replacements.
- Use a Programmable Thermostat: A programmable thermostat allows you to set different temperatures for different times of the day, maximizing energy efficiency. For example, you can lower the temperature when you’re away from home or asleep, and raise it when you’re home and awake.
- Install Low-Flow Showerheads and Faucets: Installing low-flow showerheads and faucets reduces water usage without compromising your shower experience. This conserves water and reduces your water heating costs.
- Wash Clothes in Cold Water: Washing clothes in cold water saves energy by reducing the need to heat water. Modern detergents are effective at removing stains even in cold water.
- Air Dry Clothes: Air drying clothes outdoors or indoors on a drying rack saves energy and reduces reliance on electric dryers.
- Wash Full Loads of Laundry: Washing full loads of laundry maximizes energy efficiency by reducing the number of cycles needed.
- Seal Air Leaks: Seal air leaks around windows and doors using weather stripping or caulk. This prevents warm air from escaping in the winter and cool air from escaping in the summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling.
- Use a Smart Power Strip: A smart power strip automatically cuts off power to devices that are not in use, further reducing phantom energy consumption.
- Turn Off Lights When Leaving a Room: This may seem obvious, but it’s a simple way to save energy and money.
Energy-Efficient Appliances
- Energy Star Appliances: Look for appliances with the Energy Star label, indicating that they meet energy-efficiency standards set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
- Refrigerators: Modern refrigerators are more energy-efficient than older models. Consider upgrading to a newer model if your current refrigerator is more than 10 years old.
- Dishwashers: Dishwashers can be more energy-efficient than hand washing, especially if you use energy-saving settings.
- Washing Machines: High-efficiency washing machines use less water and energy than traditional models.
- Dryers: Consider using a heat pump dryer, which uses less energy than a traditional electric dryer.
Identifying and Addressing Utility Leaks
- Check for Water Leaks: Regularly check for water leaks around sinks, toilets, and pipes. Look for signs of water damage, such as dampness or mold.
- Test Toilet Flappers: A leaking toilet can waste hundreds of gallons of water per day. To test for leaks, add a few drops of food coloring to the toilet tank and wait 15 minutes. If the color appears in the bowl, the flapper is leaking.
- Check for Air Leaks: Use a smoke pencil or a lit incense stick to identify air leaks around windows and doors.
- Inspect Pipes for Leaks: Check pipes for leaks, especially in areas that are difficult to access.
- Contact a Professional: If you suspect a leak in your plumbing or heating system, contact a qualified professional for inspection and repair.
Utilizing Renewable Energy Sources
- Solar Panels: While solar panels are typically installed on rooftops, some apartment buildings are starting to incorporate them into their design. If your building has solar panels, you may benefit from reduced electricity costs.
- Wind Energy: Wind turbines are becoming more common in urban areas. If your apartment building is located near a wind turbine, you may be able to access renewable energy.
- Green Building Practices: Apartment buildings that are designed and constructed using green building practices often incorporate energy-efficient features and renewable energy sources, resulting in lower utility costs for residents.
